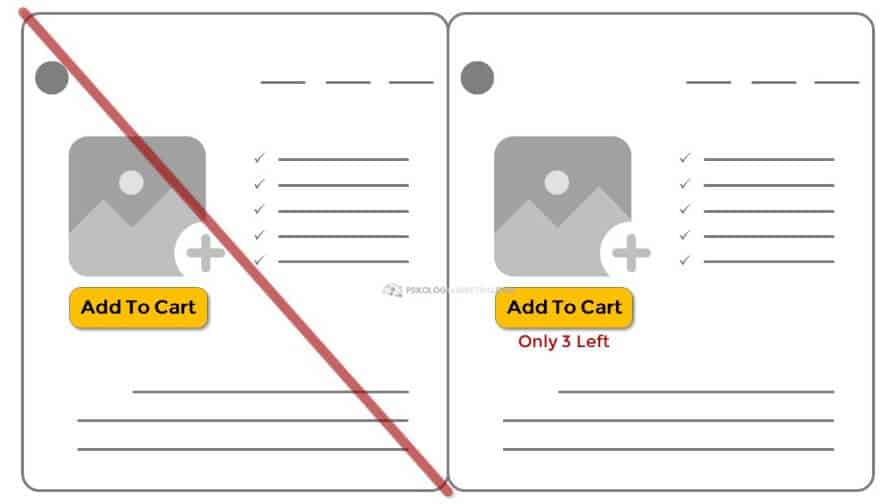
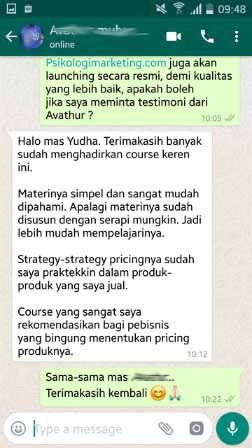
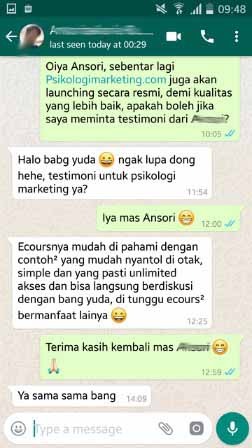
Produk Digital berupa Online Course tentang Psikologi Marketing yang dibahas berdasarkan temuan ilmiah dari jurnal internasional (bukan opini).
Anda akan mempelajari >60 unit materi berupa video maupun tulisan tentang psikologi marketing, sejauh ini sudah ada 2 kelas besar yaitu Psychology of Pricing (hasil penelitian tentang cara efektif menampilkan harga produk) dan Psychology of Conversion Optimization (hasil penelitian tentang strategi desain website yang tinggi konversi). Materi akan terus bertambah seiring temuan jurnal terbaru.
Semua materi di Psikologimarketing.com tidak ada yang berlandaskan kepada OPINI, melainkan hasil penelitian, survey, dan split test, dari para researcher luar dan dalam negeri yang bergelut di dunia marketing. Terdapat >57 Jurnal Internasional berbayar yang dikupas dalam tiap-tiap materi. Sebagian besar diantaranya berasal dari:American Marketing AssociationJournal Product & Brand ManagementJournal of Research in MarketingJournal of Applied Business ResearchJournal of Consumer ResearchJournal of MarketingMarketing Management JournalJournal of Marketing ResearchMarketing Management AssociationJournal of Marketing SciencePsychology & MarketingOrganizational Behaviour and Human Decision ProcessesJournal of RetailingJournal of Consumer Psychology
Jika Anda memiliki masalah teknis saat menggunakan platform online course dan kami gagal membantu menyelesaikan masalah tersebut, dalam jangka waktu 14 hari kami akan mengembalikan uang anda 100%.
Jaminan uang kembali hanya berlaku untuk masalah teknis saja, selain itu, semua penjualan bersifat final.